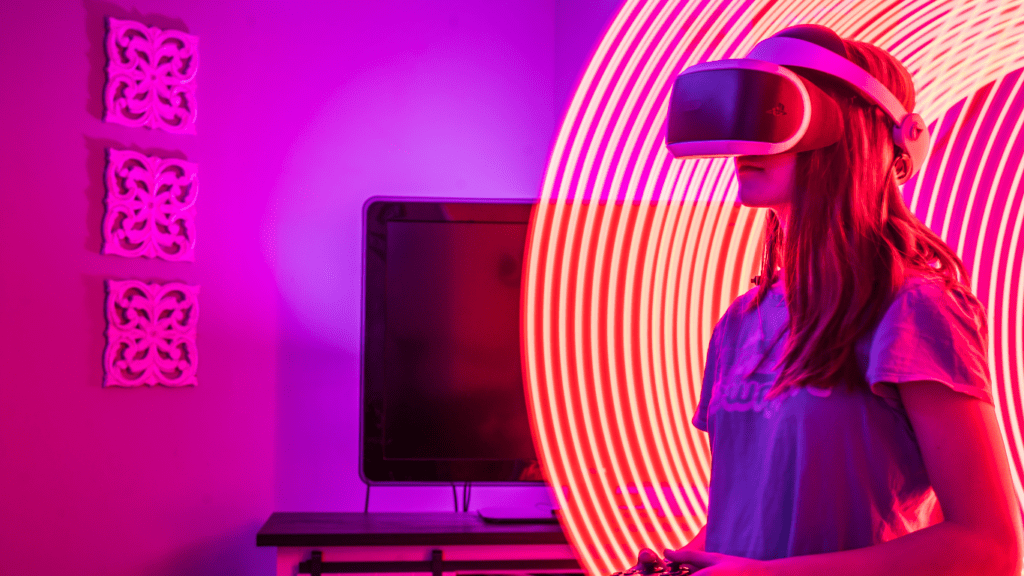
Exploring Virtual Reality in the Art World
Virtual reality has completely transformed how artists create and display their work. By using VR headsets and software, artists can construct immersive environments and intricate 3D sculptures.
These tools enable unprecedented creativity, allowing artists to experiment with new forms and mediums.
Virtual Exhibitions
VR exhibitions allow artists to showcase their work in digital galleries. These exhibitions bypass geographical constraints, letting viewers worldwide experience the art. For example, the “Acute Art” platform offers VR exhibitions from renowned artists like Jeff Koons and Marina Abramović. Users can explore these virtual galleries from their homes, making art more accessible.
Interactive Installations
Interactive installations in VR offer engaging experiences. Artists create environments that respond to viewer interaction, creating a dynamic art experience.
For instance, “The Night Cafe” allows users to step into Vincent van Gogh’s paintings, walking through the scenes and interacting with the environment. These installations provide a deeper connection between the viewer and the art.
Enhancing Creativity
VR tools empower artists to experiment without physical limitations. Software like Tilt Brush by Google lets artists paint in 3D space, creating intricate designs impossible in traditional mediums. These tools open new avenues for creativity, enabling artists to push the boundaries of their imagination.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
VR makes art more inclusive. Virtual galleries cater to individuals who can’t visit museums due to physical or geographical constraints. Projects like “The Kremer Museum” offer a completely virtual museum experience, featuring a collection of Dutch and Flemish Old Masters. This inclusivity fosters a broader appreciation and understanding of art.
Educational Applications
Educational institutions use VR to provide immersive learning experiences. Art students can explore historical art movements and techniques in a virtual setting. Programs like “VR Museum of Fine Art” allow students to study famous works up close, offering new insights and understanding.
Commercial Opportunities
Artists and galleries can monetize VR experiences. By offering virtual tours and exclusive content, they can reach a wider audience and generate additional revenue streams. Platforms like “VIVEPORT” provide artists opportunities to sell their VR art, expanding their market reach.
Preservation and Documentation
VR technology assists in preserving and documenting art. Museums and galleries can create virtual replicas of exhibitions, ensuring they are accessible for future generations. Institutions use VR to document and archive artworks, protecting them from physical degradation.
Virtual reality is revolutionizing the art world by expanding creative possibilities, enhancing accessibility, and offering new commercial opportunities. Through virtual exhibitions and interactive installations, artists engage viewers in unprecedented ways, transforming how we experience and appreciate art.
The Evolution of Art and Technology
Art and technology have always influenced each other. This synergy has grown stronger with advancements in digital tools and mediums.
From Traditional to Digital: A Brief History
Art evolved significantly from simple cave paintings to complex Renaissance masterpieces. In the 20th century, photography and film revolutionized artistic expression.
Digital art emerged in the 1960s with computer-generated graphics, and by the 1980s, artists began using software like Adobe Illustrator for creating digital works. The internet democratized art in the 1990s, allowing artists to showcase their work online. Today, technologies like virtual reality (VR) represent the newest frontier, enabling artists to create immersive, interactive experiences.
- Computer Graphics (1960s): Artists began experimenting with digital images using early computers.
- Adobe Illustrator (1987): This vector graphics editor revolutionized digital drawing and design.
- Internet Accessibility (1990s): Artists gained new platforms to share and sell their work globally.
- Digital Photography (2000s): Cameras with high resolution became accessible, transforming photography.
- 3D Printing (2000s): Enabled artists to create complex sculptures directly from digital designs.
- Virtual Reality (2010s): Artists use VR headsets and software to craft and interact with 3D art.
These milestones highlight how technology consistently expands the scope and nature of artistic expression.
How Virtual Reality Is Transforming the Art Scene
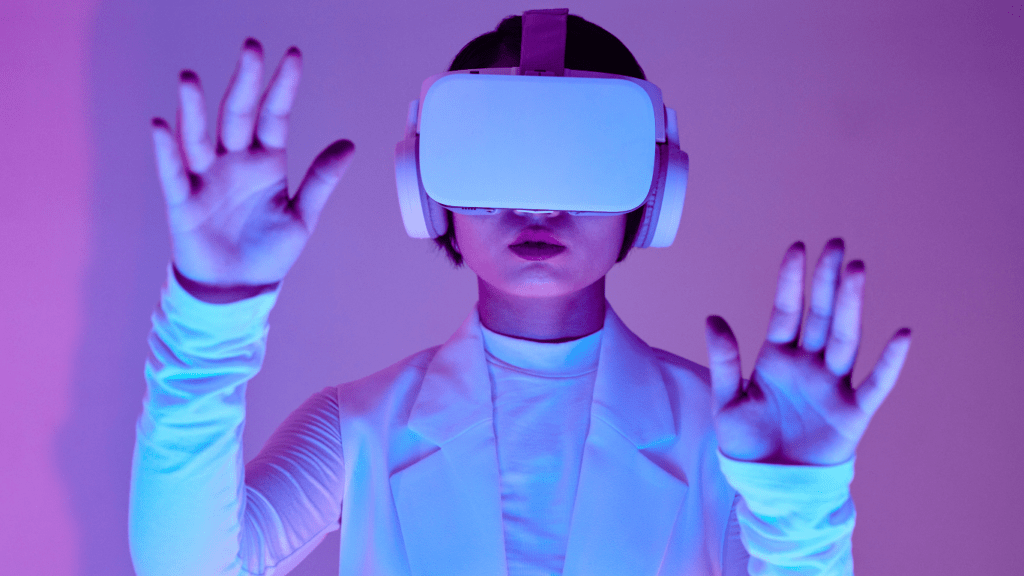

Virtual reality offers innovative dimensions for experiencing and creating art. It reshapes traditional methods and introduces new possibilities for artists and audiences alike.
Immersive Art Installations
Immersive VR installations create engaging, interactive art experiences. Artists craft environments where viewers can explore and interact with 3D elements. For instance, projects like “The Night Cafe,” inspired by Van Gogh, allow users to walk through and observe the painter’s environment in an entirely new way.
VR installations provide a sensory-rich experience, blending visual and auditory stimuli. They enable deeper emotional connections with the artwork. Viewers aren’t just passive observers; they become active participants in the art narrative.
Virtual Art Galleries and Museums
Virtual galleries and museums democratize access to art. They break down geographical barriers, offering access to collections worldwide. Prestigious museums like the Louvre and the British Museum host virtual tours, allowing users to explore exhibits from their homes.
These platforms make art education more inclusive, catering to students and art enthusiasts regardless of location. Additionally, emerging artists showcase their work in virtual galleries without needing physical space, expanding their reach to a global audience. Virtual spaces also facilitate interactive tours, with features like audio guides and curatorial notes enriching the educational experience.
The Benefits of Virtual Reality in Art
Virtual reality (VR) brings numerous advantages to the art world. Its impact is profound, transforming how artists and audiences interact with art.
Enhanced Viewer Engagement
VR enhances viewer engagement by creating immersive experiences. Viewers can walk through an artist’s virtual gallery, interacting with 3D sculptures and paintings. Applications like Tilt Brush allow artists to build intricate 3D artworks, letting viewers appreciate every minute detail by virtually stepping inside the piece.
This immersive interaction fosters a deeper connection to art. Unlike traditional methods, VR enables viewers to have personalized art experiences, tailoring their interactions based on user preferences.
Breaking Geographical Boundaries
Virtual reality breaks geographical boundaries by allowing global access to art exhibitions. Virtual galleries and museums let audiences from around the world attend exhibitions without travelling.
This democratizes art access, enabling underserved communities and individuals with mobility issues to experience high-quality art. Institutions can also host virtual tours of historical sites and renowned museums like the Louvre, offering unparalleled global reach. This accessibility supports emerging artists, providing an international platform to showcase their work without needing physical spaces.
VR not only transforms art creation but also how we experience and access it, making art more engaging and accessible to everyone.
Challenges and Considerations
When exploring VR in the art world, several challenges and considerations arise that impact both artists and audiences.
Technical Limitations and Costs
High costs and technical barriers present significant challenges. Quality VR setups, including headsets and compatible computers, are expensive, often costing over $1,000. Additionally, creating VR art demands powerful hardware and specialized software, increasing overall expenses.
Internet speed and bandwidth also affect VR experiences; slow connections can lead to lag and reduce immersion. For instance, an artist might need a high-end graphics card to render detailed 3D environments. Updates in VR technology often require continual investments to keep pace with advancements, adding to the financial burden.
Artistic Authenticity and Reception
Artistic authenticity and reception pose another set of challenges. Traditional artists might struggle to adapt to VR tools without sacrificing their unique styles. Viewers could perceive VR art as less authentic or detached from “real” artistry. VR art’s reception varies depending on public familiarity with technology.
Some audiences enthusiastically embrace interactive installations, while others find the virtual aspect less appealing. Scholars and critics often debate the legitimacy of VR as a medium within established art circles. Concerns about data privacy and screen fatigue also affect how audiences engage with VR art.
For example, an artist creating a VR painting might face skepticism regarding the authenticity compared to a traditional canvas painting.