Emerging Technologies in Virtual Reality
Exciting advancements in virtual reality (VR) continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible in digital art and interactive experiences.
Advances in VR Hardware
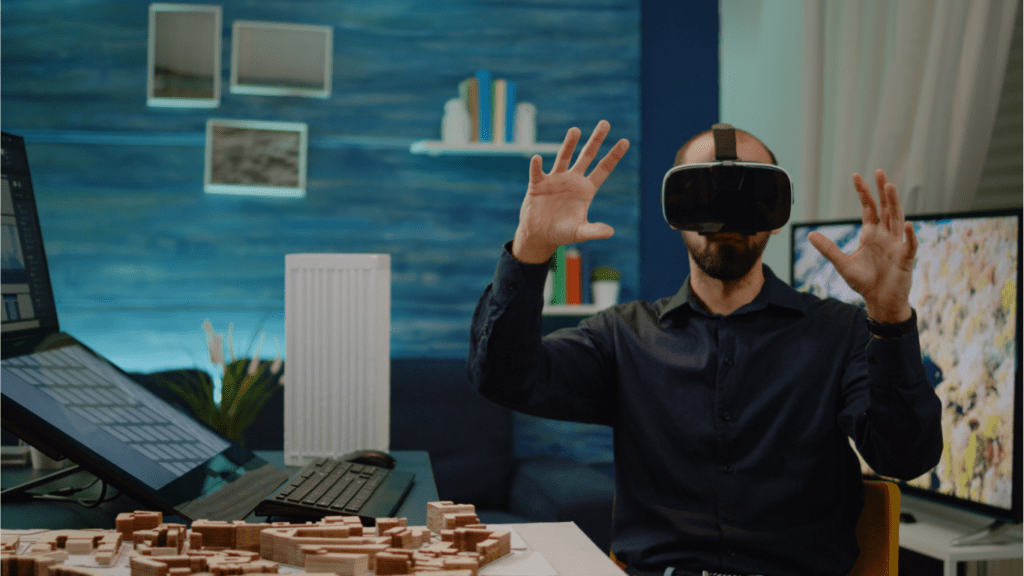
Innovations in VR hardware have significantly enhanced user experiences. High-resolution displays now offer sharper images and vivid colors, making virtual environments more lifelike. For instance, headsets like the Oculus Quest 2 and HTC Vive Pro boast improved screen resolutions and refresh rates, reducing motion sickness and increasing immersion.
Haptic feedback systems add another layer of realism. Devices such as the Teslasuit provide full-body haptic feedback, enabling users to feel physical sensations in virtual worlds.
Wireless technology also makes VR more accessible. Many headsets now operate untethered from PCs, providing greater freedom of movement and a more seamless experience.
Inclusive VR Software Developments
Inclusive software developments ensure VR experiences cater to diverse users.
- Developers focus on accessibility features, such as voice commands and adjustable text sizes, to accommodate those with disabilities.
- Software like Microsoft’s SeeingVR offers a suite of tools designed to improve VR for users with visual impairments.
- Multilingual support opens access to broader audiences.
- Applications increasingly support multiple languages, allowing non-English speakers to fully engage with the content. For example, Google Earth VR includes several language options, improving usability and reach.
- Social VR platforms create inclusive communities.
- Platforms like AltspaceVR and VRChat enable users to interact, share, and collaborate in virtual spaces, fostering connections regardless of geographical location.
Digital Art Evolution and VR Integration

Virtual reality (VR) technology transforms how digital artists create and showcase their work. This evolution allows for unprecedented interactivity and immersion.
New Tools for Digital Artists
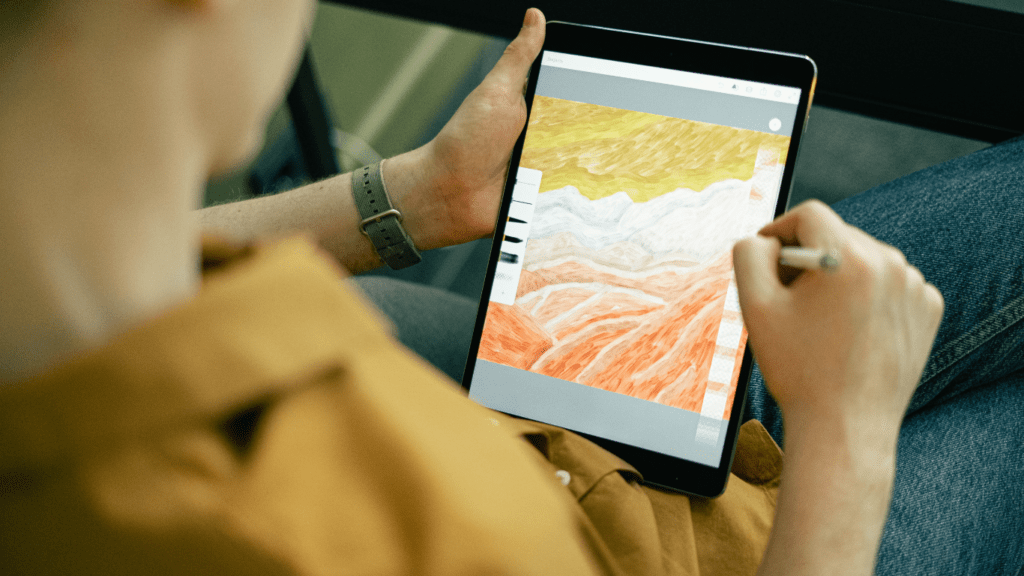
Innovative tools now enable digital artists to fully exploit VR technology. Applications like Tilt Brush and Gravity Sketch let artists paint and sculpt in a 3D space. These tools provide intuitive interfaces that replicate physical artistic techniques. Artists create intricate artworks that can be viewed from multiple angles, offering a more dynamic experience.
Tools like Quill by Oculus allow frame-by-frame animation directly inside VR, pushing creative boundaries. Updates in software continually add features like real-time collaboration, inviting a new era of artistic teamwork.
Virtual Galleries and Exhibitions
The concept of art galleries is evolving with VR. Virtual galleries allow artists to exhibit work to a global audience. These platforms, including Artland and Kunstmatrix, offer customizable virtual spaces where users interact with art pieces in a curated environment. Galleries replicate the feel of physical art spaces, enhancing user experience.
Interactive elements, such as clickable details and embedded videos, provide deeper engagement. VR headsets and web-based VR platforms extend access, letting users explore exhibitions from their homes. This shift democratizes art, making it accessible regardless of physical location.
Impact of VR on Artistic Expression
Virtual reality (VR) transforms artistic expression by offering unparalleled immersive experiences and expanding creative horizons for artists.
Enhanced Immersive Experiences
VR creates a multisensory environment, allowing artists to craft experiences that engage sight, sound, and touch. Tools like Tilt Brush and Quill let artists paint and animate in 3D space, producing artworks with depth and interactivity.
Viewers can explore these creations in virtual galleries, examining details from various angles. This not only deepens engagement but also changes how audiences perceive and interact with art.
Expanding Horizons for Artists
Artists gain access to an infinite canvas in VR, unconstrained by physical limitations. They can craft complex, large-scale works that’d be impractical in traditional settings.
VR platforms enable real-time collaboration, breaking geographic barriers and fostering global artistic teamwork. Additionally, the accessibility of virtual galleries like Artland and Kunstmatrix democratizes art exposure, allowing artists to reach diverse audiences worldwide. This integration of VR with digital art amplifies creativity, innovation, and inclusivity in the art world.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
Emerging virtual reality (VR) and digital art present new ethical concerns and challenges that need addressing. These considerations are crucial for ensuring responsible use and preservation of artistic integrity.
Privacy in Virtual Spaces
Virtual spaces introduce intricate privacy issues. In VR environments, user data, including interactions, habits, and personal information, can be collected extensively.
For instance, the extensive data collection involved in VR platforms like Oculus raises serious concerns about data security and user consent. Unauthorized access or misuse of this data can lead to exploitation or breaches, necessitating robust security measures and transparent data policies.
Intellectual Property in Digital Art
Digital art’s evolution through VR brings new intellectual property challenges. Protecting artists’ rights in a digital medium involves complexities absent in traditional art forms.
For example, digital artworks created on platforms like Tilt Brush and Quill by Oculus can be easily copied, distributed, or altered without the creator’s permission. Establishing clear, enforceable intellectual property rights is essential to prevent unauthorized reproductions and ensure artists retain control over their creations.