Exploring Virtual Reality as a New Medium for Artists
Virtual reality is reshaping the landscape for contemporary artists, providing tools to create immersive and interactive artworks. This section delves into how VR is evolving as a medium for artistic expression.
The Evolution of Artistic Mediums
Artistic mediums have always evolved, reflecting societal changes and technological advancements. From cave paintings to digital art, each era has introduced new tools and techniques.
The Renaissance brought oil paints, while the 20th century saw the rise of photography and video art. Now, in the 21st century, VR is the next frontier, enabling artists to create three-dimensional, interactive pieces that viewers can experience from within.
Defining Virtual Reality in Art
Virtual reality in art involves creating digital environments that users can navigate and interact with using VR headsets and controllers. Unlike traditional media, VR provides a sense of presence, making viewers feel as if they’re part of the artwork.
Artists use software like Tilt Brush and Medium to sculpt, paint, and animate in a virtual space. This integration of technology and creativity opens new possibilities for storytelling, audience engagement, and artistic innovation.
The Benefits of Virtual Art Spaces
Virtual art spaces radically transform how artists create and present their work, offering broader artistic possibilities and deeper audience engagement.
Enhanced Creative Freedom
Virtual reality provides artists with unparalleled creative freedom. Artists can design intricate, large-scale environments without physical constraints. For example, using tools like Tilt Brush, creators can paint in 3D space, adding elements that defy gravity and conventional mediums.
Medium lets sculptors craft detailed 3D models, giving them the freedom to experiment with textures and shapes in ways traditional materials don’t allow. Artists can also integrate interactive elements, letting viewers influence the artwork in real-time, which adds a dynamic dimension to the creative process.
Accessibility for Wider Audiences
Virtual art spaces make art more accessible to diverse audiences. Geographic and physical barriers no longer limit exposure to new artists and works.
For instance, virtual galleries can be visited from anywhere in the world, increasing audience engagement. People with disabilities benefit from this accessibility since they can explore exhibits from the comfort of their homes. Furthermore, virtual exhibitions offer curators the flexibility to update and co-curate displays effortlessly, ensuring that a broader range of art reaches a global audience.
Tools and Technologies in VR Artistry
Adopting VR for artistic expression requires specific tools and technologies. Artists need to familiarize themselves with various platforms, hardware, and software to maximize their creative potential in virtual environments.
Popular VR Platforms for Artists
Artists often use several platforms to create their VR artworks:
- Tilt Brush: Google’s Tilt Brush enables me to paint in a 3D space, using a variety of brushes and colors to produce immersive artistic pieces.
- Medium by Adobe: Medium allows me to sculpt detailed 3D models, experiment with textures, and create complex structures within VR.
- Quill: The platform, initially developed by Facebook, lets me animate my illustrations and create intricate storylines in three-dimensional space.
- Gravity Sketch: This tool gives me the freedom to design models, environments, and products in VR, promoting collaboration through cloud features.
- Masterpiece Studio: Masterpiece Studio offers a suite that combines sculpting and animation tools, helping me transform my creative ideas into reality.
Hardware and Software Requirements
Creating VR art requires robust hardware and software:
- Headsets: Devices like the Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, and PlayStation VR provide high-resolution displays and precise tracking that enhance my immersive experience.
- Computing Power: A powerful computer with a strong GPU, such as an NVIDIA GeForce RTX or AMD Radeon RX, ensures smooth performance while running VR applications.
- Controllers: Motion-tracked controllers allow me to interact with virtual environments naturally, making the artistic process intuitive and fluid.
- Software Compatibility: Ensuring that the software I choose is compatible with my hardware setup and has the necessary drivers installed is crucial for a seamless workflow.
- Storage: Adequate storage capacity, preferably SSDs, helps me manage and save large VR art files efficiently.
Equipping myself with these platforms and tools, I can explore the vast potential of virtual reality in my artistic endeavors, pushing the boundaries of creativity.
Challenges and Limitations of VR in Art
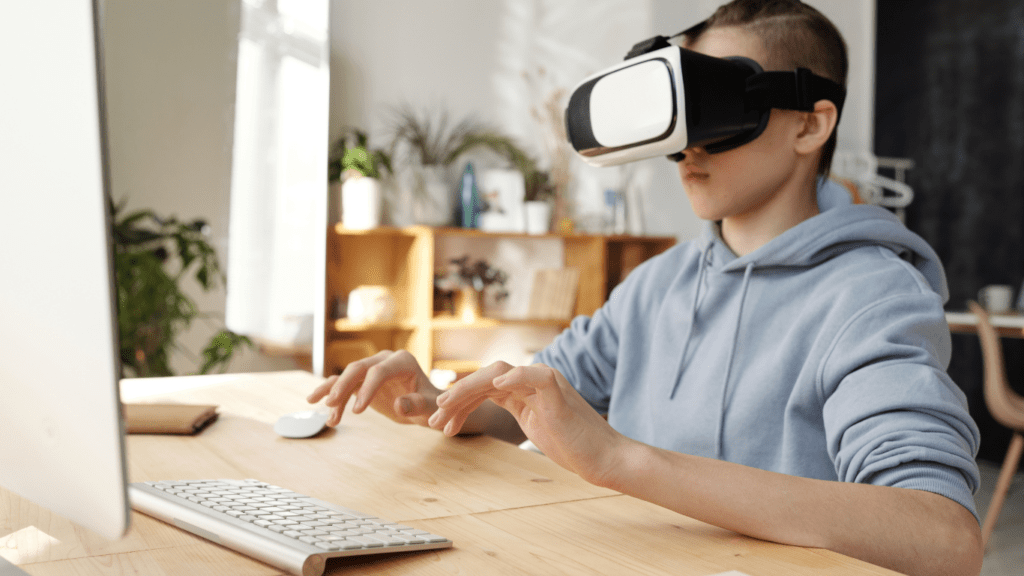

Virtual reality changes how artists create and viewers experience art. However, there are notable challenges.
Technical Barriers
High costs for VR hardware limit access for many artists. Headsets like Oculus Rift and HTC Vive cost hundreds to thousands of dollars. Moreover, advanced computing power is needed for creating and running complex VR environments.
Not all artists have top-tier computers with the necessary specs. Software compatibility also poses hurdles. Artists need VR software that works seamlessly with various devices, but fragmentation in the market can lead to compatibility issues. Lastly, storage requirements for large VR art files can be cumbersome, requiring extensive digital storage solutions.
Cultural Acceptance Issues
Widespread acceptance of VR in traditional art communities remains limited. Many art institutions favor conventional media, viewing VR as a novelty. This resistance affects the recognition and funding of VR art projects.
Additionally, the general public needs more awareness and understanding of VR art’s potential. While some tech-savvy audiences embrace it, broader acceptance takes time.
Cultural barriers also exist globally, with varying levels of technology adoption and access across regions. To overcome these, artists and institutions must work together to educate and integrate VR within the broader art world.
Case Studies: Successful VR Art Projects
Virtual reality (VR) has fostered remarkable art projects that redefine creative boundaries. Interactive VR exhibitions and renowned VR artists showcase the transformative power of this medium.
Interactive VR Exhibitions
Several VR exhibitions illustrate how immersive technology impacts the art world. The “Dreams of Dali” VR experience transports viewers into surreal environments inspired by Salvador Dali’s paintings. This project allows users to explore Dali’s art interactively, offering a new dimension to classical works.
Another significant exhibition, the “Cleveland Museum of Art’s” ARTLENS Gallery, fuses digital and physical art. Users engage with digital installations that respond to their movements. This gallery demonstrates how VR can enhance traditional art exhibitions by adding interactive, educational content.
Renowned VR Artists and Their Work
Prominent VR artists showcase the medium’s potential. Google Tilt Brush pioneer, Anna Zhilyaeva, creates live 3D paintings, bringing audiences into her artistic process in real-time. Her work exemplifies how VR enables real-time artistic exploration and audience involvement.
Laurie Anderson, a multimedia artist, uses VR to create thought-provoking pieces like the “Chalkroom.” In this VR environment, users navigate through a vast, textual landscape, combining literature and visuals. Anderson’s work highlights VR as an innovative storytelling platform.
Through these successful VR art projects, it’s evident that VR offers a unique canvas for artists, blending technology and creativity in unprecedented ways.

 Parisilyn Cruz has played a pivotal role as an article writer and key contributor in the development of Innov Art Foundry. Her deep passion for the art world is reflected in the insightful and engaging content she creates, covering everything from the latest art trends to in-depth explorations of virtual reality's impact on artistic expression. Parisilyn's writing not only informs but also inspires readers, making complex topics accessible and intriguing for a broad audience.
Beyond her writing, Parisilyn has been instrumental in shaping the direction of Innov Art Foundry. Her contributions have helped to establish the platform as a trusted resource for both seasoned artists and newcomers to the art scene. By blending her creativity with a keen understanding of the art landscape, Parisilyn Cruz has ensured that Innov Art Foundry remains at the forefront of contemporary art discourse, continually providing valuable insights and fostering a vibrant community of art enthusiasts.
Parisilyn Cruz has played a pivotal role as an article writer and key contributor in the development of Innov Art Foundry. Her deep passion for the art world is reflected in the insightful and engaging content she creates, covering everything from the latest art trends to in-depth explorations of virtual reality's impact on artistic expression. Parisilyn's writing not only informs but also inspires readers, making complex topics accessible and intriguing for a broad audience.
Beyond her writing, Parisilyn has been instrumental in shaping the direction of Innov Art Foundry. Her contributions have helped to establish the platform as a trusted resource for both seasoned artists and newcomers to the art scene. By blending her creativity with a keen understanding of the art landscape, Parisilyn Cruz has ensured that Innov Art Foundry remains at the forefront of contemporary art discourse, continually providing valuable insights and fostering a vibrant community of art enthusiasts.