Evolution of Art Installations
Art installations have evolved significantly over the years. With the advent of new technologies, especially VR, the art world has seen a revolutionary transformation.
From Traditional to Digital
Traditional art installations relied on physical mediums like paint, clay, and stone. Artists created static pieces displayed in galleries and museums. Viewers observed and interpreted these works from a distance without direct interaction.
The digital era introduced new possibilities. Digital art forms emerged, including video installations and interactive displays using sensors. These innovations allowed artists to create dynamic pieces that responded to viewer movements. This era marked the beginning of a more immersive experience, but VR took it further.
The Role of Technology in Art Evolution
Technology’s advancement has been pivotal in the evolution of art installations. High-resolution displays, motion sensors, and spatial audio components have contributed to more interactive and captivating exhibits. VR, though, has redefined what’s possible.
VR technology enables artists to construct fully immersive environments. For example, viewers can walk through Van Gogh’s “Starry Night” or explore a digitally-rendered ancient city. VR also supports multiplayer experiences where multiple users interact within the same virtual space.
This technological progress has expanded boundaries, merging digital and physical worlds seamlessly. As VR hardware continues to improve, such as higher fidelity VR headsets and more accurate motion tracking, the potential for more intricate and engaging art installations grows, inspiring new levels of creativity.
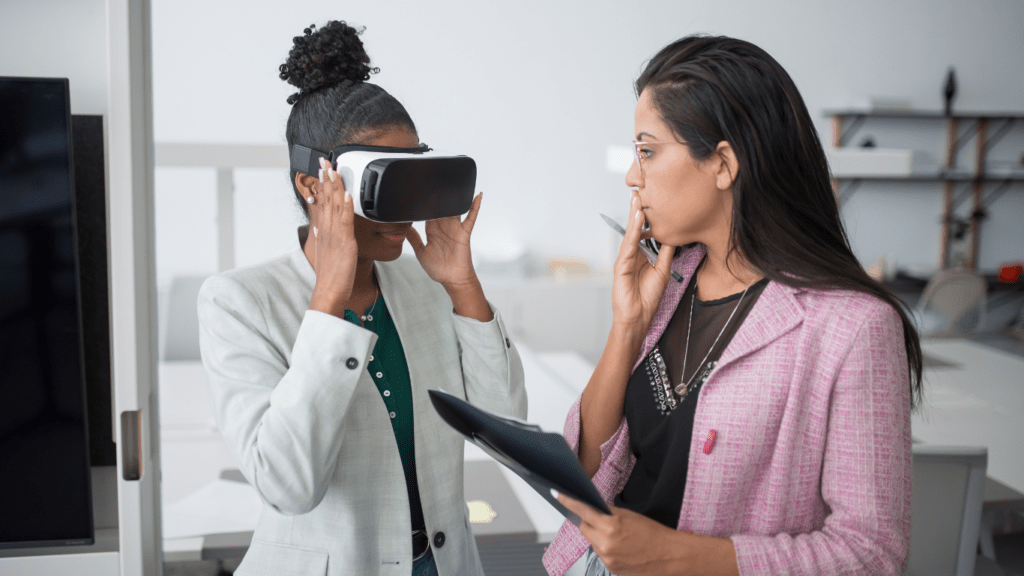
Understanding VR Technology in Art
Interactive art installations have entered a new era with the integration of VR technology. By creating immersive environments, artists can engage viewers in unprecedented ways.
Key Components of VR
1. VR Headsets
VR headsets are essential for creating immersive experiences. Advanced headsets like Oculus Quest 2 and HTC Vive Pro offer high-resolution displays and effective motion tracking.
2. Controllers
Controllers enable users to interact with the virtual environment. Devices like Oculus Touch and Valve Index Controllers enhance the tactile experience, making interactions more natural.
3. Software
Software tools like Unity and Unreal Engine power VR applications. These platforms provide artists with robust frameworks to create detailed and interactive VR installations.
4. Sensors
Sensors track user movements within the VR space. Devices such as the HTC Vive Base Stations and Oculus Sensors ensure accurate motion capture to enhance immersion.
How VR Enhances Viewer Experience
1. Immersive Environments
VR creates fully immersive environments, allowing viewers to feel present within the artwork. Users can navigate through virtual galleries or ancient cities, experiencing art in 360-degree perspectives.
2. Interactive Elements
VR installations often include:
- interactive elements
- enabling viewers to manipulate objects
- influence the environment.
This interactivity makes the experience more engaging and memorable.
3. Sensory Engagement
VR can engage multiple senses, including:
- sight
- sound
- touch
By using haptic feedback and spatial audio, artists can create a multi-sensory experience that goes beyond traditional visual art.
4. Personalized Experiences
VR allows for personalized experiences tailored to individual viewers. Users can explore at their own pace, making choices that influence the narrative or outcome of the installation.
Prominent Interactive Art Installations Using VR
VR is reshaping how we experience art through interactive installations that captivate and engage. Several prominent examples exist.
Notable Artists and Their Works
Emerging artists push VR boundaries to create immersive experiences. Olafur Eliasson merges physical and virtual elements in pieces like Rainbow, where users interact with weather phenomena.
Marina Abramović integrates VR in Rising, confronting viewers with rising sea levels to evoke emotional responses. Laurie Anderson collaborates with Hsin-Chien Huang on Chalkroom, an installation where users navigate rooms filled with floating texts.
Impact on the Art Community
VR installations transform the art community by broadening accessibility and engagement. More people experience art events globally without geographical constraints.
Galleries and museums incorporate VR to create distinctive, interactive exhibits, enhancing visitor engagement. Artists gain new tools for expression, pushing the envelope of creativity and challenging traditional art perspectives.
Challenges in Creating VR Art Installations
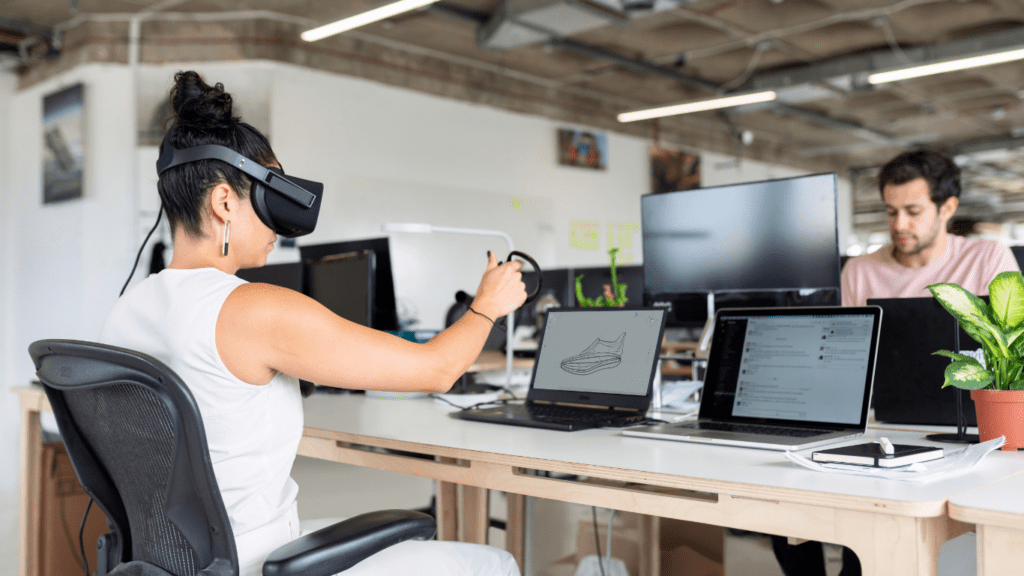

Developing interactive VR art installations involves several challenges that impact both technical execution and creative vision.
Technical Limitations
One key challenge lies in the hardware requirements. High-quality VR installations demand advanced headsets, powerful computers, and precise sensors.
Ensuring compatibility between various devices can be complex. For example, an artwork designed for the Oculus Rift might not function seamlessly with the HTC Vive.
Another limitation is the computational power needed to render immersive environments. Creating detailed, lifelike visuals requires significant processing power. Artists often encounter performance issues, such as latency or frame drops, which can detract from the immersive experience.
The software side also presents hurdles. Developing and maintaining custom VR software can be resource-intensive. Artists must balance between using existing VR platforms and developing bespoke solutions, potentially limiting creativity or increasing project timeframes.
Creative Challenges
Narrative integration within VR installations poses a significant challenge. Unlike traditional art forms, VR requires a coherent narrative that guides the viewer’s experience.
Crafting this narrative while ensuring interactivity can be complex. An excellent example is Laurie Anderson’s work, which seamlessly blends storytelling with user interaction.
Spatial design within a virtual environment also requires meticulous planning. Artists must consider how users navigate and interact within the VR space. Missteps in spatial design can lead to disorientation or reduce the overall impact of the piece.
Lastly, maintaining artistic integrity while working within the constraints of current VR technology can be difficult. Balancing the artist’s vision with practical limitations requires ingenuity and often necessitates compromise. For instance, artists such as Olafur Eliasson continuously push the boundaries to remain true to their vision while working within these constraints.
Future Trends in VR Art Installations
Virtual reality (VR) art installations continue to evolve, giving rise to new and groundbreaking trends. With advancements in technology and creative integration, the future of VR art is set to transform viewer experiences even further.
Innovations on the Horizon
Innovative tools and platforms are reshaping VR art installations. Haptic feedback devices, for instance, add a tactile dimension, allowing viewers to “feel” virtual objects. Eye-tracking technology enhances user interaction by adapting visuals based on where viewers look.
Another promising development is the use of AI to generate dynamic content. AI can create responsive environments that change according to user actions. This leads to unique, personalized experiences for every viewer. The incorporation of biometric sensors could also tailor VR experiences based on real-time emotional and physiological responses.
Integration with Other Technologies
Combining VR with other technologies unlocks novel possibilities. Augmented Reality (AR) can be used alongside VR to create mixed reality art installations. This fusion enables seamless transitions between real and virtual worlds, enriching the overall experience.
Blockchain technology offers opportunities for secure, verifiable digital art ownership. This could include tokenizing VR art pieces, allowing for unique, authenticated digital works. 5G technology also plays a crucial role, providing the high-speed, low-latency connections needed for more complex, interactive VR environments.
Use of cloud computing enables more detailed and expansive virtual worlds without requiring powerful local hardware. This integration helps make high-quality VR art more accessible to a broader audience, ensuring that technological constraints no longer limit artistic vision.