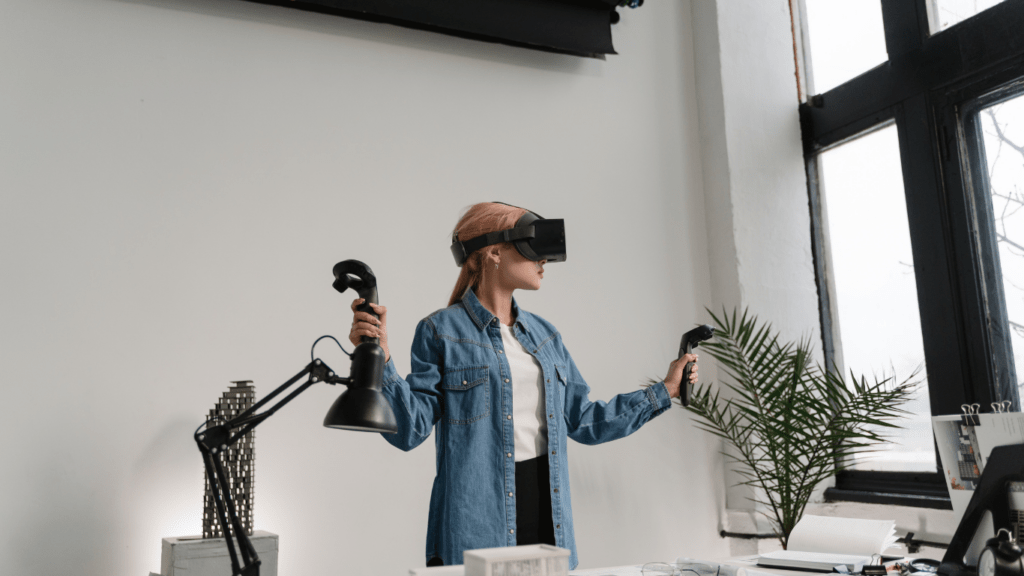
The Emergence of VR in Art Exhibitions
Virtual reality (VR) is transforming how art exhibitions are experienced. Let’s delve into the historical context and the initial impacts of VR in this domain.
Historical Context of Art Display Technologies
Art exhibitions have evolved significantly over the centuries. Initially, art was displayed in private collections, often inaccessible to the public. The concept of public museums emerged in the 18th century, democratizing access to art.
Traditional galleries and museums used physical spaces to showcase artworks, relying heavily on visual and textual information.
Advances in technology introduced new mediums for displaying art. Photography enabled the reproduction of artwork, making it more widely accessible.
Later, digital technology allowed for high-resolution images and online galleries. However, these methods lacked the immersive experience offered by VR.
The Advent of VR and Its Initial Impacts
With VR, viewers can enter a digital replica of a gallery. This technology creates a sense of presence, making the experience much more engaging. It allows for interactive elements like zooming in on details or receiving audio commentary, enhancing the educational value.
Early adopters of VR in art exhibitions, notably institutions like The British Museum and The Louvre, set the trend by offering virtual tours. These initial efforts received positive feedback, indicating a high level of user engagement and satisfaction. VR enables people to experience art without geographical constraints, making it an inclusive medium.
By offering these advanced features, VR not only replicates physical visits but often surpasses them in terms of interactivity and engagement. This shift is making art exhibitions more appealing and accessible to a global audience.
Enhancing Artistic Immersion Through VR
Virtual reality (VR) enhances artistic immersion by creating environments that let viewers deeply engage with art. This technology breaks the boundaries of traditional exhibitions.
Overcoming Physical Space Limitations
VR transcends the physical constraints of conventional art galleries.
- Art lovers can now access entire collections without physical boundaries.
- Platforms like Google Arts & Culture display famous works in high resolution.
- This digital access benefits viewers who can’t travel to exhibit locations.
- Museums might have space for only a fraction of their collections.
VR helps showcase hidden masterpieces, enhancing the diversity of artworks available for public viewing.
Introducing Interactivity with Artworks
VR enables interactive experiences where users engage directly with art. Viewers can manipulate perspectives, zoom into details, and explore art from multiple angles. Museums like The Louvre integrate VR exhibits, allowing users to virtually ‘touch’ and examine sculptures.
This interaction makes the experience more engaging and educational. Educational layers, such as historical context or artist background, can overlay the virtual exhibit, deepening understanding and appreciation.
VR Innovations in Major Art Exhibitions
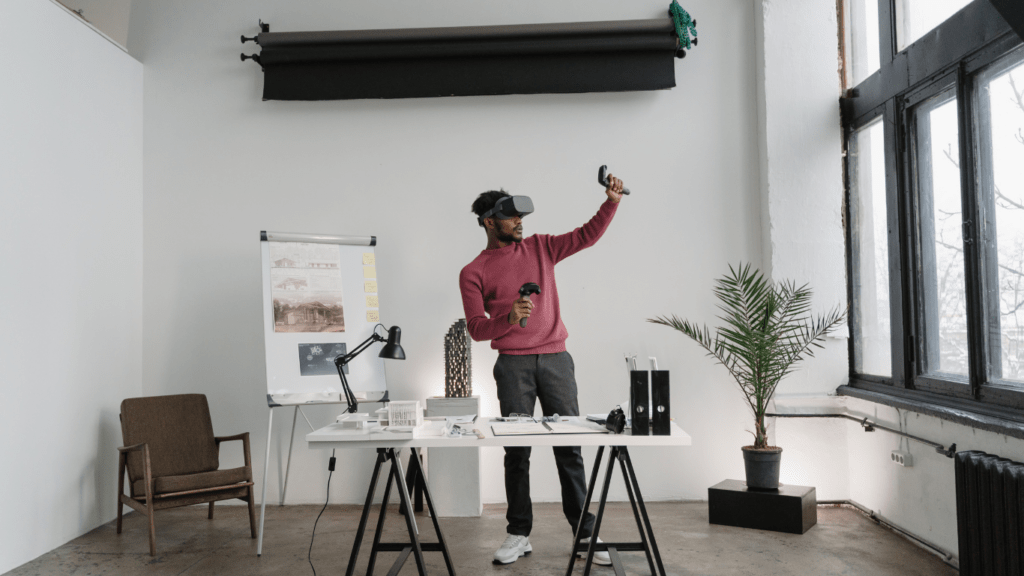

Virtual reality (VR) has brought significant advancements to art exhibitions, enabling more innovative and engaging experiences for viewers.
Case Studies of Pioneering Exhibitions
Several exhibitions have successfully integrated VR, showcasing its potential to revolutionize the art world. The British Museum’s “Virtual Reality Weekend” allowed visitors to explore a Bronze Age site, interacting with artifacts in a reconstructed ancient landscape.
The Louvre’s VR experience centered around the Mona Lisa, giving users an unprecedented close-up view and detailed analysis of the painting. Both initiatives drew significant attention, demonstrating the high potential of VR in enhancing user engagement.
Virtual Reality Tours and Their Reception
Many museums worldwide have adopted VR tours to extend their reach. Institutions such as The Art Institute of Chicago and the Musée d’Orsay offer VR tours that replicate the in-person experience.
These tours have received positive feedback for their accessibility, providing opportunities for those unable to visit in person to still enjoy and learn from world-class art collections.
VR tours often feature interactive elements and detailed narrations, which enrich the viewer’s understanding and appreciation of the artworks.
The Future of VR in Art
Virtual reality is set to play an even more significant role in the art world. Emerging trends and predictions reveal how VR’s potential in art exhibitions will evolve.
Predictions and Emerging Trends
Advancements suggest VR will continue to enhance user engagement and accessibility. As more museums and galleries adopt VR, we can expect more immersive exhibitions.
For instance, institutions will increasingly offer 3D recreations of historical art sites, enabling users to explore ancient ruins or iconic landmarks from home. Interactive elements will become more sophisticated, with haptic feedback devices allowing users to ‘feel’ the texture of sculptures or brushstrokes in a painting.
NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) might drive a new trend in digital art collecting. VR platforms will likely host virtual art auctions, where collectors can bid on exclusive virtual pieces.
Artists will benefit from global exposure without the geographical constraints of traditional exhibitions.
Potential Challenges and Open Questions
Despite the exciting prospects, several challenges lie ahead. High development costs might limit smaller galleries from adopting VR technology. The need for high-end hardware could exclude audiences lacking access to advanced devices.
Data privacy is another critical concern, as VR platforms collect vast amounts of user information.
Questions about the cultural authenticity of VR representations persist. Can VR accurately convey the experience of viewing art in person? There’s also the issue of digital preservation. How will museums maintain and update VR exhibits to prevent them from becoming obsolete?
Balancing these challenges with innovative solutions is crucial for VR’s successful integration into the art world.